radiographic testing visualize soft tissues|Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for Bone & Soft : Brand Image Formation and Radiographic Quality. 51 terms. Cassidy_Schoen6. Preview. Radiology final. 115 terms. nicoletteleighton. . this is the test of choice for diagnosing some emergency conditions. CT. this uses high frequency sound waves to visualize soft tissue. US. patients with pacemakers are unable to use this modality. MRI. Versão (3) Editar Imprimir Rolagem automática. Capotraste Não. [Intro] C Am F Dm G C Am Ao que está assentado no trono F Dm G E ao Cordeiro seja o louvor C Am Ao que está .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB359K Followers, 817 Following, 384 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Melissa D (@melissadebling)
To attain the goal of optimal treatment of patients with a soft-tissue mass, the radiologist must initially play an active role in imaging the .
The basic principles for evaluating musculoskeletal soft-tissue masses and achieving these objectives have not changed. This article addresses application of the current . Image Formation and Radiographic Quality. 51 terms. Cassidy_Schoen6. Preview. Radiology final. 115 terms. nicoletteleighton. . this is the test of choice for diagnosing some emergency conditions. CT. this uses high frequency sound waves to visualize soft tissue. US. patients with pacemakers are unable to use this modality. MRI.
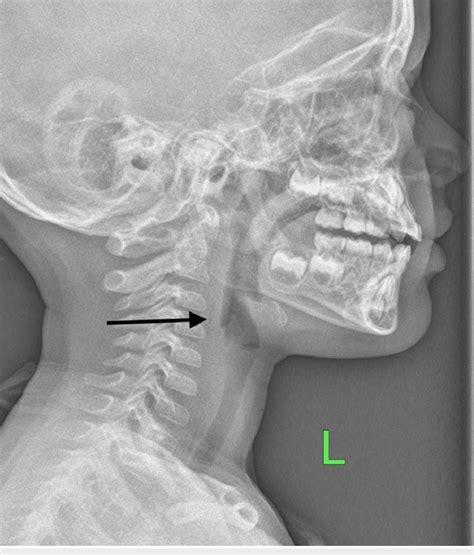
Soft-Tissue X-ray of the Neck . Plain x-ray ( Figures 4-1 and 4-2 ) provides limited information about the soft tissues of the neck.X-ray relies on differentiation of adjacent structures using four basic tissue densities: air, fat, .
Ultrasonography can detect radiolucent materials (e.g., wood, vegetation) better than radiography and computed tomography. 8, 9 Hyperechoic areas of soft tissue injury or inflammation may suggest . The detection and removal of embedded foreign bodies is often a difficult task, and foreign bodies within the soft-tissue are regularly undetected on first examination. 1 If undetected, there is a possibility of infection, long-term pain, deformities, and a reduction in functionality. 1 Wound trauma involving glass accounts for 13% of all cases presenting to the . These include adjusting the kVp and adding filters to change image contrast. Using a normal or low kVp can help visualize certain soft tissues like adenoid and effusions more clearly. High kVp is useful for exams like BA enemas where thicker tissues are involved. Digital technology also helps improve soft tissue visibility compared to .
Fluoroscopy is a real-time imaging technique that uses X-rays to visualize the body's internal structures in motion. Fluoroscopy is often used during surgeries, particularly for digestive, urinary, or reproductive systems procedures. . MRI is beneficial for visualizing soft tissues and structures, such as the brain, spinal cord, muscles, and . In this chapter, the physical principles of X-rays are introduced. We start with a general definition of X-rays compared to other well known rays, e. g., the visible light. In Sec. 7.2, we will learn how X-rays can be generated and how they can be characterized with respect to their energy. The most relevant concept to understand how X-ray imaging works is the . Mammography is a special type of X-ray test used to examine breast tissue. Enlarged heart. This sign of congestive heart failure shows up clearly on X-rays. Blocked blood vessels. Injecting a contrast material that contains iodine can help highlight sections of the circulatory system so they can be seen easily on X-rays. Abdomen. Digestive .
Various soft tissues, such as muscle and subcutaneous soft tissue, are usually included in the views obtained on radiography of the musculoskeletal system. Radiographs are largely limited in the assessment of muscle abnormalities, with rare exceptions such as myositis ossificans which shows typical radiographic appearances but may be . The value of retropharyngeal soft tissue measurements in trauma of the adult cervical spine. Cervical spine soft tissue measurements. Skeletal Radiol. 1987;16:98–104. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Costelloe CM, Madewell JE. Radiography in the initial diagnosis of primary bone tumors. Background In this study, we aimed to determine the prevalence and radiographic features of incidental head and neck soft tissue calcifications (STCs) on panoramic imagesand assess their clinical .Electrodiagnostic Testing . Bones, calcifications, some tumors, and other dense matter appear white or light because they absorb the radiation. Less dense soft tissues and breaks in bone let radiation pass through, making these parts look darker on the X-ray film. . The MRI tool uses magnetic fields and a sophisticated computer to take high .
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) – Unveiling the Soft Tissues. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI, is a non-invasive imaging technique that excels at capturing detailed images of soft tissues like the brain, muscles, and organs. Unlike X-rays and CT scans, which use ionizing radiation, MRI relies on the principles of magnetism and radio waves.These differences allow us to distinguish between soft tissue structures. For example, when imaging a lateral elbow at 55 kVp, it is easier to visualize the fat pads from muscle. This is important because these fat pads can fill with fluid subsequent to a traumatic injury and may be the only visible sign of an elbow fracture.However, above 60 .
soft tissue radiography
The phrase “soft tissues are unremarkable” plays a significant role in describing the condition of certain body structures. . CT scans, and MRIs allow healthcare professionals to visualize internal body structures and assess their condition. . Please read the disclaimer Can not rule out something on an imaging test is a phrase that is . The intra oral examination is divided into soft tissue and hard tissue examination. The soft tissue examination will be focused on for the purpose of this article. Similarly to the extra oral .This paper presents an algorithm for segmentation of computed radiography (CR) images of extremities into bone and soft tissue regions. The algorithm is a region-based one in which the regions are constructed using a growing procedure with two different statistical tests. Following the growing process, tissue classification procedure is . Radiographic Diagnosis. Visual-tactile examination of carious lesions is not sufficient for assessing interproximal or occlusal surfaces. Therefore, radiography is commonly used to assess and detect caries, as it gives the practitioner additional information about the clinical progression. . Soft tissues are not as calcified as bone or teeth .
how hard is the vtne test
Computed radiography versus indirect digital radiography for the detection of glass soft-tissue foreign bodies N. Sheridan a, b, *, J.P. McNulty a a Radiography and Diagnostic Imaging, School of Medicine, University College Dublin, Health Sciences Centre, Belfield, Dublin 4, Ireland b X-Ray (Radiology) Department, The Adelaide and Meath Hospital, Dublin, Incorporating the . Soft tissue abscesses are focal or localized collections of pus caused by an immune response to pathogenic microorganisms. They are surrounded by a peripheral rim or abscess membrane and can be found within the soft tissues in any body part 1. . Radiographic features Plain radiograph.
Radiographic Imaging Techniques MCQs October 12, 2024 October 12, 2024 by u930973931_answers Which of the following imaging techniques uses ionizing radiation to create images of the body?
how hard is the w3 html test
Soft Tissue
Osteomyelitis is a multifaceted disease characterized by inflammation of bone and marrow. While various etiologies of osteomyelitis have been documented, it is almost always secondary to infection. Osteomyelitis may occur through direct inoculation of bacteria into the bone, hematogenous spread from distant sites of infection, or the contiguous spread from . As the beams go through your body, bones, soft tissues and other structures absorb radiation in different ways. Solid or dense objects (such as bones) absorb radiation easily, so they appear bright white on the image. Soft tissues (such as organs) don’t absorb radiation as easily, so they appear in shades of gray on the X-ray.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like a positively charged electron, never occurs during radiographic procedures, radiolucent and more. hello quizlet Study tools
What is the primary purpose of radiographic imaging? A) To measure blood pressure B) To visualize internal structures of the body C) To detect changes in heart rate D) To measure bone density.
This test gives the best soft tissue contrast of all the imaging modalities. MRI This scan produces a computer generated cross-sectional image in the axial plane. Plain Films. The initial choice for foreign body detection is plain film radiography, which is the imaging modality of choice due to its ability to detect most foreign bodies quickly and cheaply with relatively low radiation exposure. Objects denser than soft tissue will attenuate more rays and, therefore, appear in greater contrast to the surrounding areas.
Soft

Assista em Apple TV+. Um menino de 12 anos é o único sobrevivente de um acidente. Enquanto ele e outras pessoas afetadas pela tragédia tentam compreender o que .
radiographic testing visualize soft tissues|Musculoskeletal Ultrasound for Bone & Soft